Introduction:
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on pilonidal sinus, a condition that affects the skin near the cleft of the buttocks. Whether you’re experiencing symptoms or seeking preventive measures, our website provides unique insights to help you understand, manage, and prevent pilonidal sinus.
What is the Pilonidal Sinus?
Pilonidal sinus is a common condition characterized by the formation of a small tunnel or sinus tract in the skin near the cleft of the buttocks. These sinuses can become filled with hair, debris, and bacteria, leading to infection and inflammation. Pilonidal sinuses often cause pain, swelling, and drainage of pus.
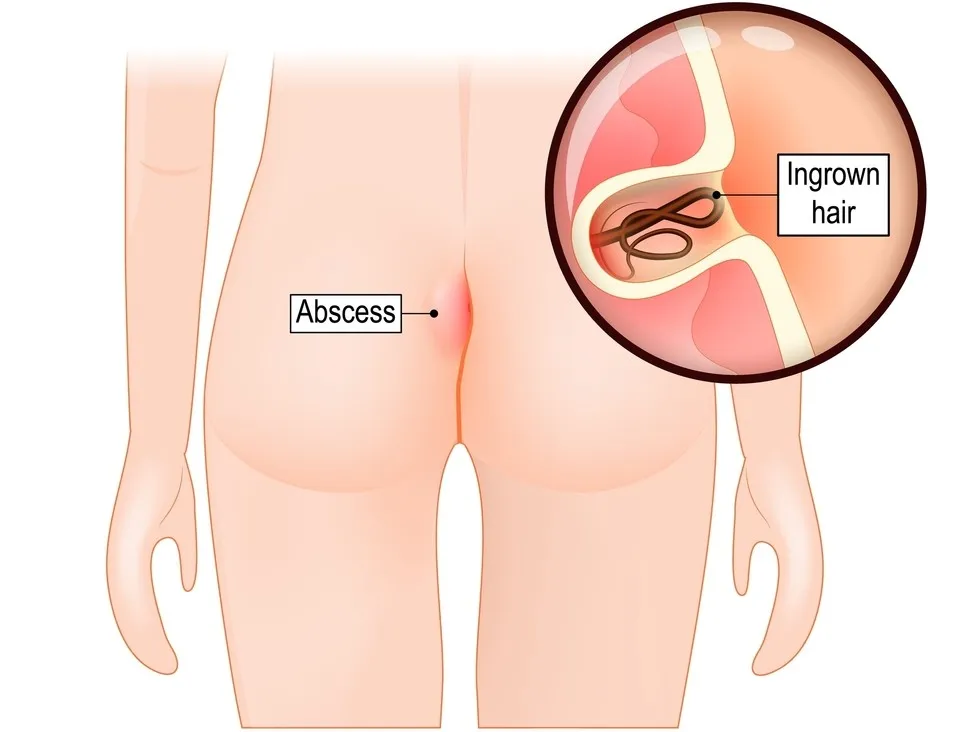
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of pilonidal sinus is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development, including:
- Ingrown hairs: Hair follicles trapped in the skin can lead to the formation of sinus tracts.
- Friction: Activities that involve prolonged sitting or rubbing against the buttocks may irritate the skin and increase the risk of pilonidal sinus.
- Poor hygiene: Inadequate cleansing of the buttock area can lead to the accumulation of dirt, sweat, and bacteria, contributing to infection.
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing pilonidal sinuses.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of pilonidal sinus may include:
- Pain or tenderness in the buttock area
- Swelling or redness around the sinus opening
- Drainage of pus or blood from the sinus tract
- Fever or chills if the sinus becomes infected
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing pilonidal sinus typically involves a physical examination of the affected area. Your healthcare provider may also order imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, to assess the extent of the sinus tract and rule out other conditions.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for pilonidal sinus depends on the severity of symptoms and the presence of infection. Common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: If the sinus is infected, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear the infection.
- Incision and drainage: In cases where there is a large abscess or significant pus accumulation, a procedure to drain the pus may be performed.
- Excision surgery: For recurrent or chronic pilonidal sinuses, surgical removal of the sinus tract and surrounding tissue may be necessary to prevent recurrence.
Prevention:
Preventing pilonidal sinus involves maintaining good hygiene and reducing factors that contribute to its development, such as:
- Regularly washing the buttock area with soap and water
- Keeping the buttock area clean and dry, especially after sweating or physical activity
- Avoiding prolonged sitting or activities that may cause friction in the buttock area
- Shaving or waxing the hair around the cleft of the buttocks to reduce the risk of ingrown hairs
Conclusion:
Pilonidal sinus can be a painful and bothersome condition, but with proper understanding, treatment, and preventive measures, it can be managed effectively. Our website aims to provide you with the information and resources you need to navigate pilonidal sinus with confidence and ease. If you’re experiencing symptoms or have concerns about pilonidal sinus, consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and care.
