Introduction:
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on hemorrhoids, a common yet often misunderstood condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Whether you’re seeking information on symptoms, treatment options, or prevention strategies, our website aims to provide you with all the essential details you need to know about hemorrhoids. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this condition and empower you with knowledge for effective management and relief.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
- Definition: Define hemorrhoids as swollen and inflamed veins in the rectum or anus, often causing discomfort, itching, and sometimes bleeding.
- Types of Hemorrhoids: Explain the distinction between internal hemorrhoids (inside the rectum) and external hemorrhoids (under the skin around the anus).
- Causes: Explore the various factors contributing to the development of hemorrhoids, including straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation or diarrhea, pregnancy, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
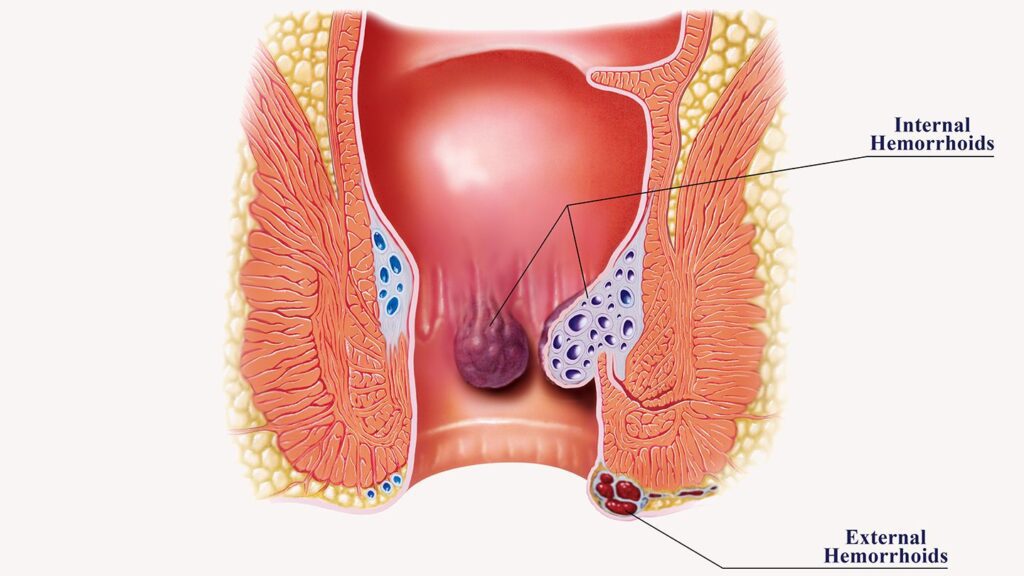
Signs and Symptoms:
- Common Symptoms: Detail the typical signs of hemorrhoids, such as rectal bleeding, itching, pain, swelling, and a lump near the anus.
- Grading System: Introduce the grading system used by healthcare professionals to classify hemorrhoids based on severity, ranging from Grade I (mild) to Grade IV (severe).
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- Medical Examination: Describe the diagnostic process for hemorrhoids, which may involve a physical examination of the anal area, a digital rectal exam, and in some cases, a visual inspection using a proctoscope or anoscope.
- Differential Diagnosis: Discuss how healthcare providers differentiate hemorrhoids from other conditions with similar symptoms, such as anal fissures, anal abscesses, and colorectal cancer.
Treatment Options:
- Conservative Management: Outline conservative measures for managing mild hemorrhoids, including dietary modifications (increased fiber intake), topical treatments (creams, ointments), and sitz baths to relieve discomfort and promote healing.
- Procedures and Interventions: Explore minimally invasive procedures, such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, infrared coagulation, and hemorrhoidectomy, for treating more severe or persistent hemorrhoids.
- Lifestyle Changes: Emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining regular bowel habits, staying hydrated, avoiding prolonged sitting or straining, and incorporating physical activity into daily routines to prevent hemorrhoid recurrence.
Prevention Strategies:
- Dietary Recommendations: Offer dietary tips to promote bowel regularity and prevent constipation, including consuming fiber-rich foods (fruits, vegetables, whole grains), staying hydrated, and limiting intake of processed foods and caffeine.
- Healthy Habits: Encourage the adoption of healthy lifestyle habits, such as avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, practicing proper hygiene (gentle cleansing after bowel movements), and engaging in regular exercise to support overall colon health.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- Red Flags: Highlight symptoms or signs that may indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring prompt medical evaluation, such as persistent rectal bleeding, severe pain, or changes in bowel habits.
- Importance of Consultation: Stress the significance of consulting a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations, especially if symptoms persist or worsen despite self-care measures.
Conclusion:
Empowered with knowledge about hemorrhoids, you are better equipped to navigate the challenges associated with this common condition. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, exploring treatment options, and implementing preventive strategies, you can take control of your health and find relief from hemorrhoidal discomfort. Remember, seeking timely medical advice and adopting healthy lifestyle habits are key steps toward managing hemorrhoids effectively and improving your overall well-being.
